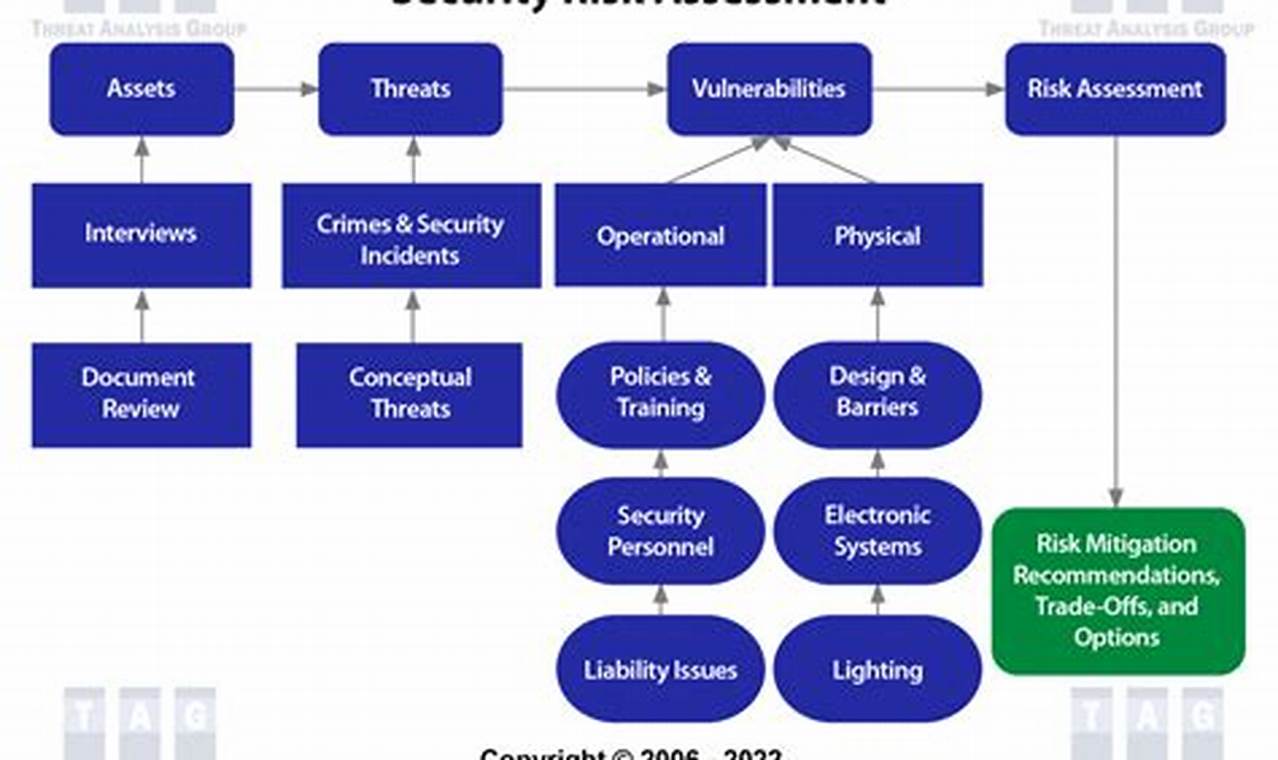
Security risk management is a crucial aspect of safeguarding sensitive information and critical assets against potential threats and vulnerabilities. It involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that could compromise the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of an organization’s assets and operations.
Effective security risk management is vital as it helps organizations prioritize and address their most critical risks, ensuring business continuity, reputational protection, and compliance with regulatory requirements. It enables organizations to allocate resources efficiently, make informed decisions, and reduce the likelihood and impact of potential incidents.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the key components of security risk management, explore best practices, and discuss its importance in various industries and contexts.
Security risk management
Security risk management is a critical process that helps organizations identify, assess, and mitigate risks that could compromise the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of their assets and operations. To effectively manage security risks, it is important to consider the following key aspects:
- Identification
- Assessment
- Mitigation
- Monitoring
- Continuous improvement
- Governance
- Communication
- Training
These aspects are interconnected and interdependent, forming a comprehensive framework for security risk management. By effectively addressing each of these aspects, organizations can enhance their overall security posture and reduce the likelihood and impact of potential security incidents.
Identification
Identification is the initial and fundamental step in security risk management, as it involves recognizing and understanding the potential threats and vulnerabilities that could impact an organization’s assets and operations. This process requires a comprehensive understanding of the organization’s environment, including its mission, objectives, and risk appetite.
- Asset identification: Identifying and categorizing the organization’s assets, both physical and intangible, is crucial for understanding the potential impact of risks. This includes hardware, software, data, intellectual property, and personnel.
- Threat identification: Threat identification involves recognizing and understanding the potential sources of harm that could exploit vulnerabilities and compromise assets. This includes natural disasters, cyberattacks, human error, and malicious insiders.
- Vulnerability identification: Identifying vulnerabilities involves examining weaknesses or gaps in an organization’s security controls that could be exploited by threats. This includes weaknesses in software, hardware, processes, and personnel.
- Risk identification: Risk identification involves combining the identified threats and vulnerabilities to determine the potential risks that could impact the organization. This includes assessing the likelihood and impact of each risk.
Effective identification of security risks enables organizations to prioritize their efforts and resources, focusing on the most critical risks that require immediate attention. It also provides a foundation for developing and implementing appropriate risk mitigation strategies.
Assessment
Assessment is a critical component of security risk management, as it involves evaluating the identified risks and determining their potential impact on an organization’s assets and operations. This process helps organizations prioritize their security efforts and allocate resources effectively.
Risk assessment involves analyzing the likelihood and impact of each identified risk. Likelihood refers to the probability of a risk occurring, while impact refers to the potential consequences of the risk. By assessing these factors, organizations can determine the overall risk level and prioritize their response.
There are various methods for conducting risk assessments, including qualitative and quantitative approaches. Qualitative assessments rely on subjective judgments and expert opinions, while quantitative assessments use numerical data and statistical analysis to evaluate risks. The choice of method depends on the nature of the risks and the availability of data.
Effective risk assessment enables organizations to make informed decisions about risk mitigation strategies. It helps them identify the most critical risks that require immediate attention and allocate resources accordingly. Regular risk assessments are essential for organizations to stay abreast of changing risk landscapes and ensure the effectiveness of their security controls.
Mitigation
Mitigation is a crucial component of security risk management, involving the implementation of measures to reduce the likelihood and impact of identified risks. It plays a vital role in safeguarding an organization’s assets and operations from potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Effective risk mitigation requires a comprehensive understanding of the identified risks and their potential consequences. Organizations must prioritize risks based on their likelihood and impact, and allocate resources accordingly. Mitigation strategies should be tailored to the specific risks and may include a combination of technical, administrative, and physical controls.
Technical controls involve implementing technological measures to prevent or detect and respond to security incidents. This includes firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption. Administrative controls involve establishing policies and procedures to manage security risks. This includes security awareness training, access controls, and disaster recovery plans. Physical controls involve implementing physical measures to protect assets and personnel. This includes access control systems, security guards, and video surveillance.
By implementing effective mitigation strategies, organizations can significantly reduce the likelihood and impact of security incidents. Mitigation is an ongoing process that requires regular review and updates to ensure its effectiveness in the face of evolving threats and vulnerabilities.
Monitoring
Monitoring is a critical component of security risk management, as it involves the ongoing observation and analysis of an organization’s security posture to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities. Effective monitoring enables organizations to detect and respond to security incidents in a timely manner, minimizing their impact on operations and assets.
Security monitoring involves the use of various tools and technologies to collect and analyze data from multiple sources, including network traffic, system logs, and security devices. This data is analyzed to identify anomalies, suspicious activities, and potential security breaches. Real-time monitoring allows organizations to detect and respond to security incidents as they occur, preventing or mitigating their impact.
Regular monitoring is essential for organizations to stay abreast of changing risk landscapes and ensure the effectiveness of their security controls. It provides valuable insights into the organization’s security posture, enabling proactive risk management and threat detection. Monitoring also facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements and industry best practices, demonstrating an organization’s commitment to information security.
Continuous improvement
Continuous improvement is an essential aspect of security risk management, as it enables organizations to proactively identify and address emerging threats and vulnerabilities. This iterative process involves regularly reviewing and updating security controls, policies, and procedures to ensure their effectiveness in the face of evolving risk landscapes.
Security risk management is a dynamic field, and new threats and vulnerabilities are constantly emerging. Continuous improvement allows organizations to stay ahead of these threats by proactively identifying and addressing them. Regular risk assessments and monitoring can help organizations identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments to their security posture.
For example, an organization may implement a new security tool to enhance its threat detection capabilities. As part of the continuous improvement process, the organization would regularly review the effectiveness of the tool and make adjustments as needed. This could involve fine-tuning the tool’s configuration, integrating it with other security systems, or providing additional training to staff on its use.
Continuous improvement is a critical component of effective security risk management, as it enables organizations to proactively manage their security posture and adapt to changing risk landscapes. By embracing a continuous improvement mindset, organizations can significantly reduce the likelihood and impact of security incidents, protecting their assets, operations, and reputation.
Governance
Governance plays a pivotal role in shaping an organization’s security risk management framework. It establishes the structures, processes, and responsibilities for managing security risks effectively, ensuring alignment with the organization’s overall goals and objectives.
-
Board Oversight
The board of directors is ultimately responsible for overseeing the organization’s security risk management program. They provide strategic guidance, ensure adequate resources are allocated, and hold management accountable for the effectiveness of the program.
-
Management Responsibility
Senior management is responsible for implementing and maintaining the security risk management program. This includes developing and implementing policies, procedures, and controls, as well as ensuring that risks are identified, assessed, and mitigated effectively.
-
Internal Audit
Internal audit plays a critical role in evaluating the effectiveness of the organization’s security risk management program. They conduct independent assessments to provide assurance that the program is operating as intended and that risks are being managed appropriately.
-
Regulatory Compliance
Governance also involves ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations related to security risk management. Organizations must adhere to industry standards and best practices to demonstrate their commitment to information security and protect themselves from legal liabilities.
Effective governance fosters a culture of security awareness and accountability throughout the organization. It provides a clear framework for managing risks, ensuring that they are identified, assessed, and mitigated in a timely and appropriate manner. This helps organizations maintain a strong security posture, protect their assets and operations, and build trust with stakeholders.
Communication
Communication plays a critical role in security risk management, enabling organizations to effectively identify, assess, mitigate, and respond to security risks. Clear and timely communication is essential for ensuring that all stakeholders are aware of their roles and responsibilities in managing security risks.
Ineffective communication can lead to misunderstandings, confusion, and delayed responses to security incidents. For example, if an employee is unaware of the organization’s security policies and procedures, they may inadvertently introduce risks by clicking on malicious links or sharing sensitive information. Similarly, if management fails to communicate the importance of security to employees, they may not prioritize security measures, increasing the organization’s vulnerability to attacks.
Effective communication involves establishing clear channels of communication, defining roles and responsibilities, and providing regular training and updates on security risks. Organizations should also foster a culture of open communication, where employees feel comfortable reporting security concerns and asking questions. This helps to identify and address potential risks early on, preventing them from escalating into major incidents.
In summary, communication is a vital component of security risk management, enabling organizations to effectively manage security risks and protect their assets and operations. By establishing clear channels of communication, defining roles and responsibilities, and fostering a culture of open communication, organizations can significantly improve their security posture and reduce the likelihood of security incidents.
Training
Training plays a critical role in security risk management by equipping individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to identify, assess, mitigate, and respond to security risks. It is a fundamental component of any comprehensive security risk management program, as it enables organizations to build a workforce that is aware of security risks and capable of taking appropriate actions to protect the organization’s assets and operations.
Effective training programs provide employees with a thorough understanding of the organization’s security policies and procedures, as well as the potential security risks that the organization faces. This training helps employees to recognize and avoid common security threats, such as phishing attacks, malware, and social engineering scams. It also provides employees with the skills necessary to respond to security incidents, such as data breaches or cyberattacks, in a timely and effective manner.
For example, a study by the Information Systems Security Association (ISSA) found that organizations with well-trained employees are significantly less likely to experience security breaches. The study also found that trained employees are more likely to report security concerns to management, which can help to identify and address potential risks before they escalate into major incidents.
In summary, training is an essential component of security risk management. By providing employees with the knowledge and skills necessary to identify, assess, mitigate, and respond to security risks, organizations can significantly improve their security posture and reduce the likelihood of security incidents.
Security Risk Management FAQs
Security risk management is a crucial aspect of protecting an organization’s assets and operations from potential threats and vulnerabilities. It involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information and systems.
Question 1: What are the key components of security risk management?
Answer: The key components of security risk management include identification, assessment, mitigation, monitoring, continuous improvement, governance, communication, and training.
Question 2: Why is risk assessment important in security risk management?
Answer: Risk assessment helps organizations prioritize risks, allocate resources effectively, and select appropriate mitigation strategies. It provides a comprehensive understanding of the likelihood and potential impact of various risks.
Question 3: How does monitoring contribute to security risk management?
Answer: Monitoring involves ongoing observation and analysis of an organization’s security posture to detect potential threats and vulnerabilities. It enables timely detection and response to security incidents, minimizing their impact.
Question 4: What is the role of governance in security risk management?
Answer: Governance provides a framework for managing security risks, ensuring alignment with organizational objectives. It establishes structures, processes, and responsibilities for overseeing the security risk management program.
Question 5: How does training contribute to effective security risk management?
Answer: Training equips individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to identify, assess, mitigate, and respond to security risks. It helps build a security-aware workforce capable of protecting the organization’s assets and operations.
Question 6: What are the benefits of implementing a comprehensive security risk management program?
Answer: A comprehensive security risk management program helps organizations protect their critical assets, comply with regulatory requirements, reduce the likelihood and impact of security incidents, and build trust with stakeholders.
Summary: Security risk management is a critical and ongoing process that enables organizations to proactively identify, assess, mitigate, and respond to potential threats and vulnerabilities. Implementing a comprehensive security risk management program is essential for protecting an organization’s assets, operations, and reputation.
Transition: To learn more about security risk management best practices and strategies, explore the following sections of this article.
Security Risk Management Tips
Implementing effective security risk management strategies is crucial for protecting an organization’s assets and operations. Here are several key tips to consider:
Tip 1: Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
Regular risk assessments help organizations identify potential threats, vulnerabilities, and their associated risks. This enables them to prioritize risks and allocate resources effectively.
Tip 2: Implement Multi-Layered Security Controls
Organizations should implement a combination of technical, administrative, and physical security controls to protect against various types of threats. This multi-layered approach enhances overall security posture.
Tip 3: Foster a Security-Aware Culture
Educating employees about security risks and their responsibilities is critical. By fostering a security-aware culture, organizations can reduce the likelihood of human error and insider threats.
Tip 4: Use Security Monitoring and Logging Tools
Security monitoring tools continuously monitor systems and networks for suspicious activities. Logging tools record events and activities for analysis and incident response.
Tip 5: Establish an Incident Response Plan
Having a well-defined incident response plan ensures organizations can respond to security incidents quickly and effectively, minimizing their impact.
Tip 6: Conduct Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits help organizations evaluate the effectiveness of their security controls and identify areas for improvement. This proactive approach strengthens the overall security posture.
Summary: By following these tips, organizations can significantly enhance their security risk management practices and protect their critical assets and operations from potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Conclusion: Security risk management is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, assessment, and improvement. By adopting a proactive and comprehensive approach, organizations can build a robust security posture and safeguard their information, systems, and reputation.
Conclusion
Security risk management is a critical aspect of protecting an organization’s assets and operations. This article has explored key components, best practices, and tips to effectively manage security risks. By understanding the potential threats and vulnerabilities, organizations can prioritize risks, allocate resources, and implement appropriate mitigation strategies.
A comprehensive security risk management program is essential for safeguarding information, systems, and reputation. It fosters a culture of security awareness, enhances incident response capabilities, and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements. Organizations must continuously monitor, assess, and improve their security posture to stay ahead of evolving threats and vulnerabilities.
Youtube Video: