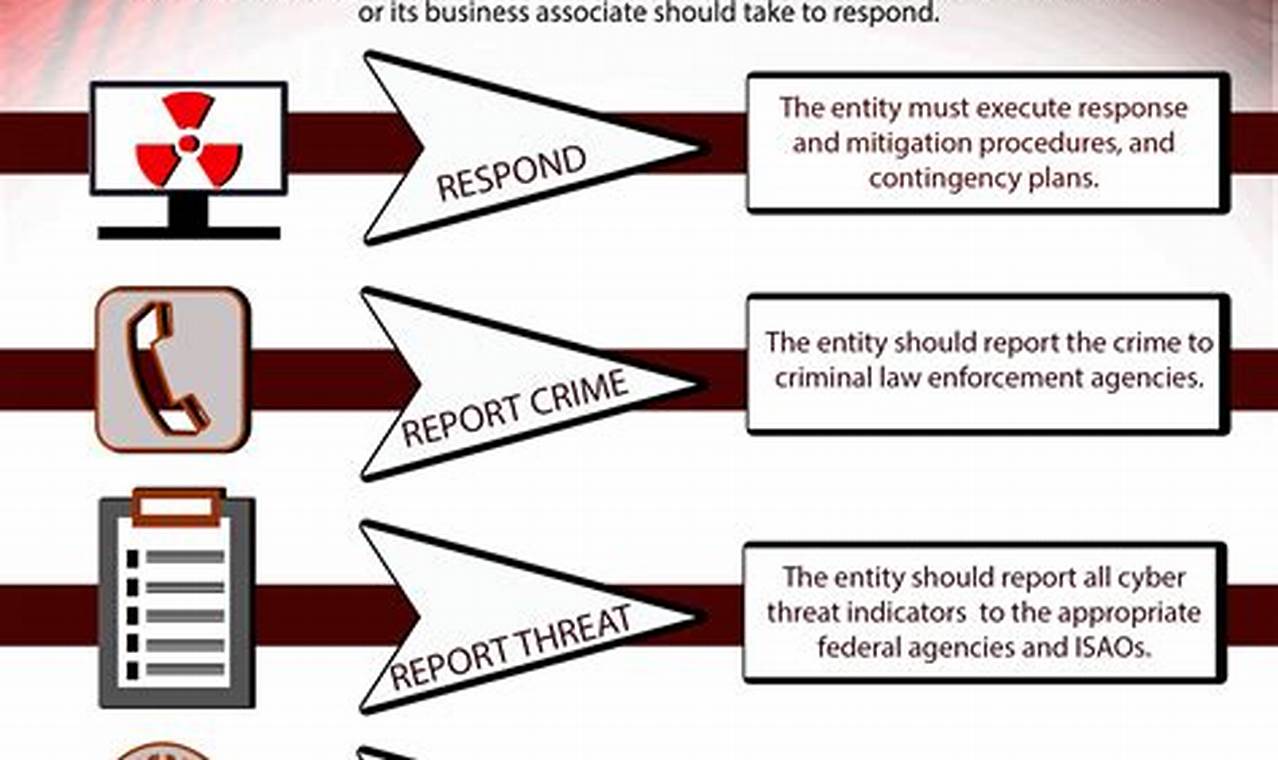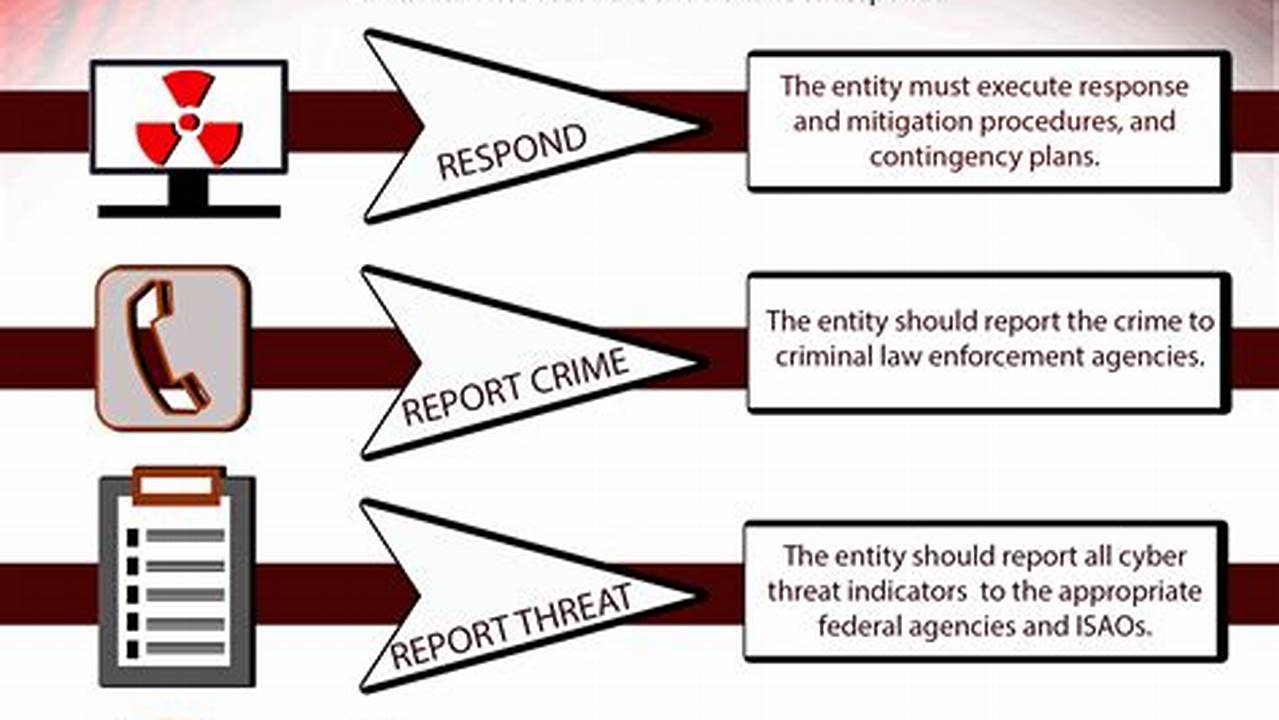
Cyber threat response encompasses the processes and procedures designed to identify, analyze, and mitigate cyber threats. These threats can manifest in various forms, such as malware attacks, phishing scams, or unauthorized access attempts to networks and systems.
Implementing a robust cyber threat response plan is crucial for organizations to protect their sensitive data, maintain operational efficiency, and uphold customer trust. By swiftly identifying and responding to cyber threats, organizations can minimize potential damage, reduce downtime, and maintain business continuity.
The field of cyber threat response has evolved significantly in recent years, driven by the increasing sophistication of cyber threats and the growing reliance on technology across industries. Organizations must stay abreast of the latest cyber threat intelligence and best practices to effectively safeguard their digital assets.
Cyber threat response
Cyber threat response encompasses a comprehensive range of activities aimed at safeguarding organizations from the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. Six key aspects underpin an effective cyber threat response strategy:
- Identification: Detecting and recognizing potential cyber threats
- Analysis: Assessing the nature, scope, and impact of identified threats
- Mitigation: Implementing measures to neutralize or contain threats
- Prevention: Establishing proactive measures to minimize the risk of future threats
- Response: Developing and executing plans to address and recover from cyber incidents
- Recovery: Restoring systems and data to a secure state after a cyber incident
These aspects are interconnected and interdependent, forming a holistic approach to cyber threat response. By effectively addressing these aspects, organizations can significantly enhance their resilience against cyber threats and protect their critical assets.
Identification
Identification, as the initial step in cyber threat response, plays a critical role in safeguarding organizations from the detrimental impacts of cyber threats. It involves the continuous monitoring and analysis of systems, networks, and data to detect suspicious activities or anomalies that may indicate a potential threat. The ability to identify threats promptly allows organizations to respond swiftly, minimizing the risk of damage and disruption.
Consider a scenario where an organization successfully identifies an ongoing phishing campaign targeting its employees. By detecting the malicious emails and recognizing the telltale signs of phishing attempts, the organization can promptly alert its employees, preventing them from falling victim to the scam. This proactive identification and response can significantly reduce the risk of sensitive data being compromised or financial losses due to fraudulent transactions.
In conclusion, the identification of potential cyber threats serves as the cornerstone of an effective cyber threat response strategy. By investing in robust threat detection and monitoring capabilities, organizations can enhance their overall security posture and proactively mitigate the risks associated with cyber threats.
Analysis
Within the context of cyber threat response, analysis plays a pivotal role in determining the appropriate course of action. It involves thoroughly examining identified threats to understand their nature, scope, and potential impact on the organization.
- Threat Characterization: Identifying the type of threat (e.g., malware, phishing, ransomware) and its technical characteristics allows responders to select the most effective mitigation strategies.
- Scope Assessment: Determining the extent of the threat, including the number of affected systems, data, or users, helps prioritize response efforts and allocate resources accordingly.
- Impact Analysis: Evaluating the potential consequences of the threat, such as data loss, financial damage, or reputational harm, guides decision-making and resource allocation.
- Vulnerability Identification: Identifying vulnerabilities or weaknesses in systems or processes that the threat exploits assists in developing targeted mitigation measures and long-term preventive strategies.
Through comprehensive analysis, organizations can gain a clear understanding of the threat landscape, enabling them to make informed decisions, prioritize response actions, and allocate resources effectively. This process contributes to a more agile and efficient cyber threat response, minimizing the potential impact of threats on the organization’s operations and reputation.
Mitigation
Mitigation, as a crucial component of cyber threat response, involves implementing measures to neutralize or contain identified threats. Its significance lies in preventing or minimizing the potential damage caused by cyberattacks.
Upon threat analysis, organizations can select and deploy appropriate mitigation strategies based on the nature and severity of the threat. These strategies may include:
- Deploying security patches or updates to address vulnerabilities
- Implementing firewalls or intrusion detection systems to block malicious traffic
- Employing anti-malware software to detect and remove malicious code
- Isolating infected systems to prevent the spread of threats
- Implementing data backups to recover lost or compromised data
Effective mitigation strategies not only neutralize immediate threats but also strengthen an organization’s overall security posture, making it more resilient against future attacks. For instance, by promptly patching vulnerabilities, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of exploitation by threat actors.
In conclusion, mitigation plays a vital role in cyber threat response by preventing or minimizing the impact of identified threats. Organizations must prioritize mitigation strategies as part of their comprehensive cyber threat response plan to safeguard their systems, data, and reputation.
Prevention
Prevention forms a critical pillar within cyber threat response, focusing on establishing proactive measures to minimize the risk of future threats. It involves implementing strategies and practices that strengthen an organization’s security posture and reduce the likelihood of successful cyberattacks.
- Vulnerability Management: Regularly identifying and patching vulnerabilities in systems and software can significantly reduce the attack surface available to threat actors.
- Security Awareness Training: Educating employees about cyber threats and best practices can help prevent human errors that could lead to security breaches.
- Network Segmentation: Dividing a network into smaller segments can limit the potential impact of a breach, preventing attackers from gaining access to sensitive data across the entire network.
- Regular Backups: Maintaining backups of critical data ensures that information can be restored in the event of a cyberattack or data loss.
By adopting a proactive approach to prevention, organizations can significantly enhance their overall cybersecurity posture. Prevention measures complement other aspects of cyber threat response, such as detection, analysis, and mitigation, creating a holistic and robust defense against cyber threats.
Response
Response, as an integral part of cyber threat response, encompasses the development and execution of plans to effectively address and recover from cyber incidents. It involves a series of coordinated actions aimed at minimizing the impact of cyber threats and restoring normal operations.
- Incident Response Plan: A comprehensive plan outlining the steps to be taken in the event of a cyber incident, including roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and containment procedures.
- Cyber Incident Management: The process of coordinating and managing the response to a cyber incident, including triage, containment, eradication, and recovery.
- Forensic Investigation: The systematic examination and analysis of data to determine the cause and extent of a cyber incident, identify the responsible parties, and gather evidence for legal or insurance purposes.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery: The plans and procedures in place to ensure the continuity of critical business functions and the recovery of data and systems in the event of a cyber incident.
These facets of response are interconnected and interdependent, forming a comprehensive framework for addressing and recovering from cyber incidents. Effective response plans enable organizations to minimize downtime, protect sensitive data, and maintain customer trust in the face of cyber threats.
Recovery
Recovery, as a crucial aspect of cyber threat response, encompasses the processes and procedures involved in restoring systems and data to a secure state after a cyber incident. It plays a pivotal role in minimizing the impact of cyber threats and ensuring business continuity.
- Data Restoration: Recovering lost or compromised data through backups or alternative sources to ensure the continuity of critical business operations.
- System Restoration: Rebuilding and reconfiguring affected systems to ensure they are secure and free of vulnerabilities, preventing further compromise.
- Incident Review and Analysis: Conducting a thorough analysis of the cyber incident to identify its root cause, determine its impact, and implement measures to prevent similar incidents in the future.
- Communication and Transparency: Communicating openly and transparently with stakeholders, including customers, employees, and regulatory authorities, about the incident and the recovery process.
These facets of recovery are interconnected and essential for organizations to effectively respond to and recover from cyber incidents. By implementing robust recovery plans and procedures, organizations can minimize downtime, protect sensitive data, maintain customer trust, and ensure business continuity in the face of cyber threats.
Cyber Threat Response FAQs
This FAQ section addresses common concerns and misconceptions regarding cyber threat response to enhance understanding and promote effective practices.
Question 1: What is the primary objective of cyber threat response?
Answer: Cyber threat response aims to minimize the impact of cyber threats, protect sensitive data, maintain business continuity, and safeguard an organization’s reputation.
Question 2: Why is it crucial to have a comprehensive cyber threat response plan?
Answer: A comprehensive plan provides a structured approach to incident management, ensuring a swift and effective response, minimizing downtime, and facilitating recovery.
Question 3: What are the key elements of an effective cyber threat response strategy?
Answer: Key elements include threat identification, analysis, mitigation, prevention, response, and recovery, working together to enhance an organization’s overall.
Question 4: How can organizations stay up-to-date with the evolving cyber threat landscape?
Answer: Continuous monitoring of threat intelligence, industry best practices, and security advisories is essential for adapting to the dynamic nature of cyber threats.
Question 5: What is the role of employee awareness in cyber threat response?
Answer: Educating employees about cyber threats and best practices empowers them to recognize and report suspicious activities, playing a vital role in prevention and early detection.
Question 6: How can organizations measure the effectiveness of their cyber threat response plans?
Answer: Regular testing, performance analysis, and post-incident reviews help organizations assess the effectiveness of their plans and identify areas for improvement.
In conclusion, cyber threat response is a critical aspect of cybersecurity, enabling organizations to proactively address and mitigate cyber threats, ensuring business continuity, protecting sensitive data, and maintaining customer trust.
Explore additional sections of this article to delve deeper into specific aspects of cyber threat response and enhance your understanding of this crucial topic.
Cyber Threat Response Best Practices
Implementing a robust cyber threat response strategy is essential for organizations to protect their sensitive data, maintain operational efficiency, and uphold customer trust. Here are several crucial tips to enhance your cyber threat response capabilities:
Tip 1: Establish a Comprehensive Cyber Threat Response Plan
A well-defined plan outlines roles and responsibilities, incident reporting procedures, containment measures, and recovery strategies. This plan should be regularly reviewed and updated to align with evolving threats and technological advancements.
Tip 2: Invest in Continuous Monitoring and Threat Intelligence
Real-time monitoring of systems and networks, coupled with access to threat intelligence feeds, enables organizations to promptly detect and respond to potential threats. This proactive approach helps prevent incidents and minimize their impact.
Tip 3: Implement Multi-Layered Security Controls
Deploying a combination of security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and anti-malware software, creates a layered defense against cyber threats. These controls complement each other to provide comprehensive protection.
Tip 4: Regularly Patch and Update Systems and Software
Unpatched vulnerabilities offer entry points for attackers. Promptly applying security patches and updates strengthens an organization’s security posture and reduces the risk of successful cyberattacks.
Tip 5: Conduct Regular Security Audits and Risk Assessments
Periodically assessing the security posture of systems, networks, and applications helps identify vulnerabilities and areas for improvement. These assessments provide valuable insights for enhancing the overall security of the organization.
Tip 6: Train Employees on Cybersecurity Awareness
Educating employees about cyber threats and best practices empowers them to recognize suspicious activities and report them promptly. This human element is vital in preventing and mitigating cyber threats.
Tip 7: Establish a Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Plan
Cyber incidents can disrupt business operations. Having a comprehensive plan in place ensures that critical functions can be restored quickly, minimizing downtime and maintaining continuity.
Tip 8: Conduct Regular Incident Response Drills and Exercises
Testing incident response plans through drills and exercises helps identify gaps, improve coordination, and enhance the overall effectiveness of the response strategy.
By following these best practices, organizations can significantly strengthen their cyber threat response capabilities, proactively address emerging threats, and protect their critical assets from potential damage.
Remember, cyber threat response is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, adaptation, and improvement. By embracing these tips, organizations can enhance their resilience against cyberattacks and safeguard their operations.
Conclusion
Cyber threat response is an indispensable component of an organization’s cybersecurity strategy, enabling it to effectively prevent, detect, and mitigate cyber threats. Through continuous monitoring, rapid response, and proactive measures, organizations can safeguard their sensitive data, maintain operational efficiency, and uphold customer trust in the face of evolving cyber threats.
The dynamic nature of cyber threats demands a vigilant and adaptive approach to response. By embracing best practices, investing in robust security controls, and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness, organizations can strengthen their resilience against cyberattacks and protect their critical assets. The ongoing battle against cyber threats requires organizations to remain proactive, agile, and committed to continuous improvement.
Youtube Video: